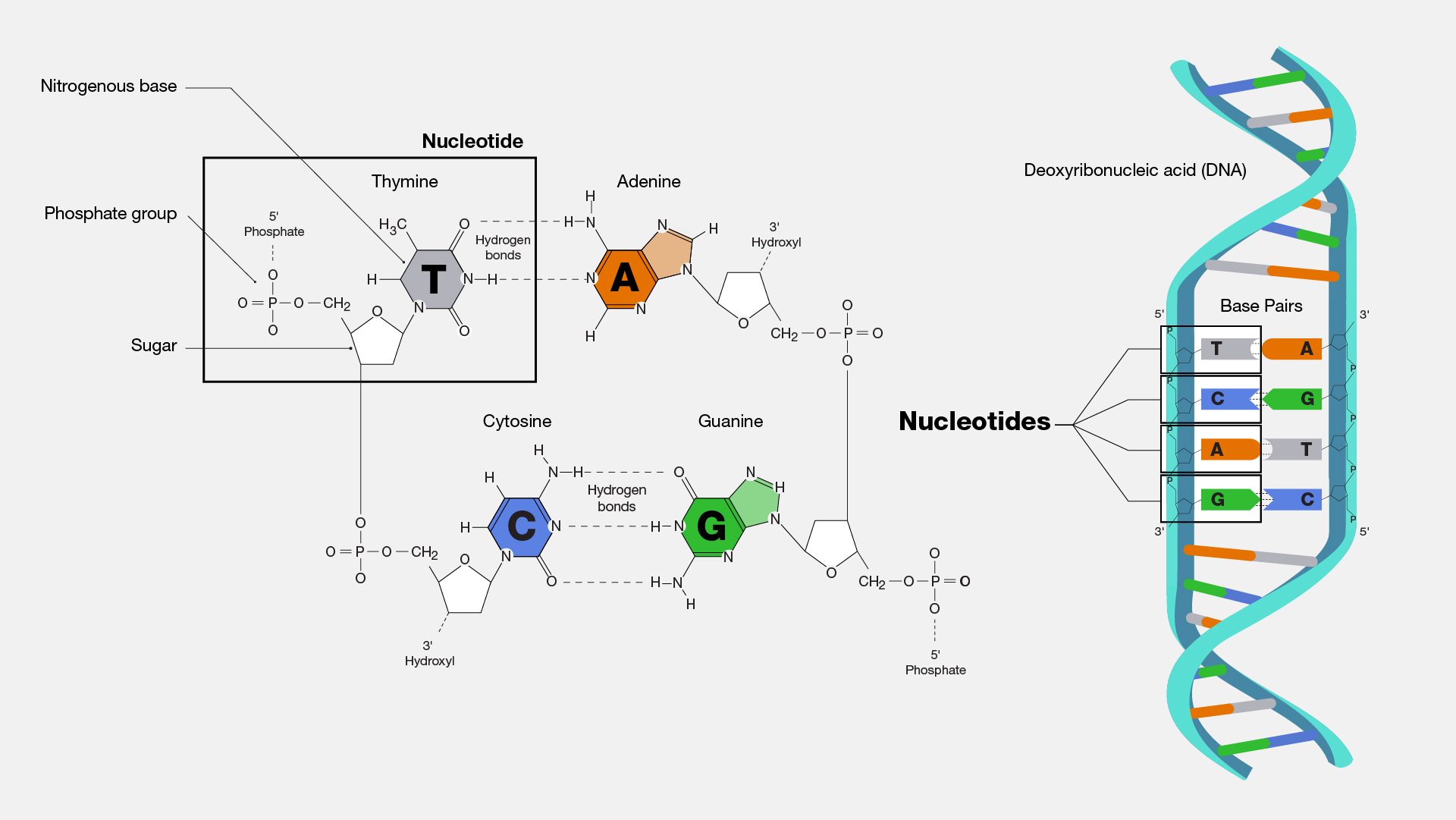
Basic Unit of Dna
Generally the more cMs shared between individuals the more genetically related they are. As the template strand moves through the enzyme it is unravelled and RNA nucleotides are added to the growing mRNA molecule.
Find out about autosomal x chromosome y chromosome and mitochondrial DNA.

. By controlling the production of mRNA within the nucleus the cell regulates the rate of gene expressionIn this article we will. We would like to show you a description here but the site wont allow us. Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic DNA Replication.
Solving the The Fundamental Unit of Life Multiple Choice Questions of Class 9 Science Chapter 5 MCQ can be of extreme help as you will be aware of all the concepts. The Fundamental Unit Of Life Class 9th By ADHWEAT GUPTA 1. Adenine A cytosine C guanine G and thymine T.
The basic repeating structural and functional unit of chromatin is the nucleosome which contains eight histone proteins and about 146 base pairs of DNA Van Holde 1988. All living things bananas and people included pass on information from one generation to the next using the same basic material DNAWithin every living organism most cells contain a. Use our web-based Purify app to select chromatography columns and resins configure ÄKTA systems and find accessories.
DNA Polymerase II. These MCQ Questions on The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 with answers pave for a quick revision of the Chapter thereby helping you to enhance subject knowledge. DNA is a two-stranded molecule.
It belongs to Type B or Family B of the polymerases. APIdays Paris 2019 - Innovation scale APIs as Digital Factories New Machi. AB Knowledge and Employability Science 10-4 2006.
CELL BASIC UNIT OF LIFE Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Multicellular Organisms Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Cell Organelles Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuoles Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Apparatus Nucleus Chromosomes Basic Structure Number. Extracting DNA from a Banana and Other Fruits. This mRNA then exits the nucleus where it acts as the basis for the translation of DNA.
The DNA of a cell holds all the information that a cell needs to keep itself alive. Its major function is the 3 5 exonuclease activity and to also restart replication after replication stops due to DNA strand damages. The RNA primer typically is 15-50 bases long.
Every cell is different but there is a basic structure that is common to all cells. A cell is essentially genetic material in a gel-like substance surrounded by a membrane. A basic part is a functional unit of DNA that cannot be subdivided into smaller component parts.
Energy flow metabolism and biochemistry occurs within cells. Rather than RNA polymerase moving along the DNA strand the DNA moves through the RNA polymerase enzyme. Common applications of liquid chromatography systems are purification of mRNA for vaccines proteins DNA plasmids mAb and viral vectors.
The 4 Types of DNA and Molecular Genealogy DNA analysis can help build the family tree. The structure of DNA is dynamic along its length being capable of coiling into tight loops and other shapes. The DNA polymerase II is found in the replication fork to help in directing the activities of other polymerases.
Two complementary bases located on opposing DNA strands. A composite part is a functional unit of DNA consisting of two or more basic parts assembled together. DNA primase has molecular weight 60000 Dalton and contains only a single subunit which functions synthesize RNA primers.
Cell Division Genetics and Molecular Biology. Once it reaches the terminator sequence the process terminates and the newly synthesised RNA strand is released. The cell is the fundamental unit of structure and function in all living organisms.
The activity of an organism depends on the total activity of independent cells. Your genome is made of a chemical called deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA for short. DNA transcription is the process by which the genetic information contained within DNA is re-written into messenger RNA mRNA by RNA polymerase.
CELL BASIC UNIT OF LIFE 2. DNA is a long polymer made from repeating units called nucleotides each of which is usually symbolized by a single letter. How do I know which type of chromatography instrument is right for my needs.
Human DNA is over 60 identical to banana DNA. DNA Replication StepsStages Initiation. In all species it is composed of two helical chains bound to each other by hydrogen bonds.
AB Biology 30 2007 Updated 2014 12 Unit C. Either A T C or G. Transcription Unit is a stretch of a DNA transcribed into an RNA molecule.
The section of DNA or the gene that is transcribed is known as the transcription unit. One type of DNA used in genetic genealogy that utilizes the 22 nonsex chromosomes. DNA contains four basic building blocks or bases.
The region between one set of origin and termination sites is called a replication unit or replicon within which one event of. Heat stress increased the expression of ZBP1 through heat shock transcription factor 1 HSF1 and activated ZBP1 through a mechanism independent of the nucleic acid. The DnaB helicase and DnaG primase constitute a functional unit within the replication complex called the Primosome.
Although the basic mechanism remains the same eukaryotic DNA replication is much more complex and involves a higher number of proteins and enzymes. DNA synthesis is initiated within the template strand at a specific coding region site known as origins. This is the stage where DNA replication is initiated.
A unit of measurement for DNA segments. BBa_R0051 is an example of a basic part a promoter regulated by lambda cl. The origin sites are targeted by the initiator proteins which recruit additional proteins that help in the replication process to form a replication complex around the DNA origin.
The word lysis means to separate. The order or sequence of these bases form the instructions in the genome. Cells contain DNA which is found specifically in the chromosome and RNA found in the cell nucleus and cytoplasm.
The genetic material of cells is found as molecules called DNA. The DNA-dependent RNA polymerase binds to the promoter and catalyses the polymerization in the 5 to 3 direction on the template strand. The basic steps for extracting DNA are the same no matter what the cell type.
We found that Z-DNA binding protein 1 ZBP1 a Z-nucleic acid receptor mediated heatstroke by triggering receptor-interacting protein kinase 3 RIPK3-dependent cell death.

What Are The 3 Parts Of A Nucleotide Biology Notes Biochemistry Notes Dna

Chemical Structure Of Dna Chemical Structure Biochemistry Science Chemistry

Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks
Comments
Post a Comment